Kubernetes cluster architecture
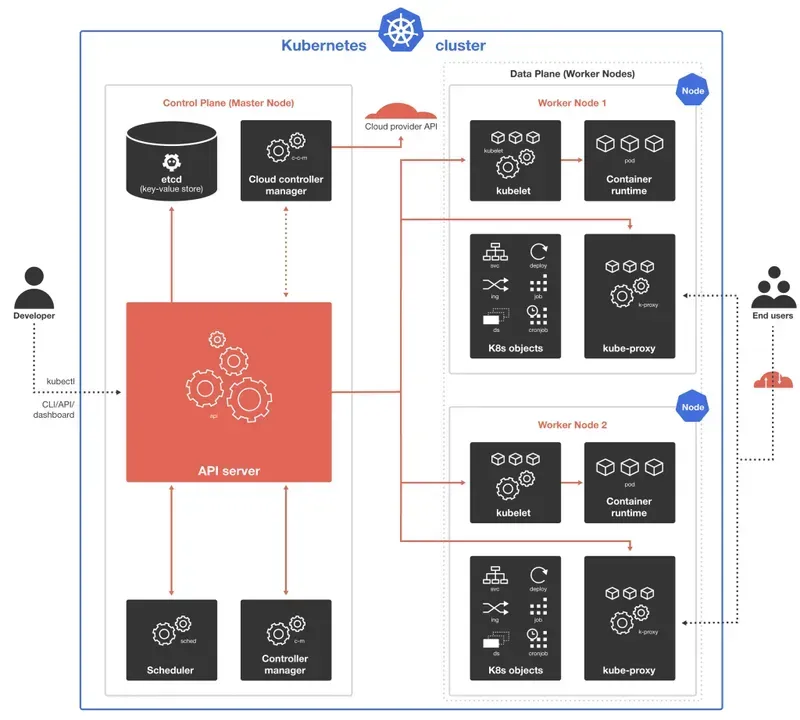
Each Kubernetes cluster consists of at least one master instance, called a control plane, and several worker nodes, which run the cluster orchestration system. The head nodes and worker nodes can represent virtual or physical computers or cloud instances.
Control plan
The control plane is intended to supervise worker instances and run the Kubernetes API server, scheduler and all major controllers. All administrative aspects, such as interaction between cluster elements, persistence of cluster state and workload scheduling are managed in the master node. Speaking of production environments, the master node runs across a number of machines and a cluster runs across a number of nodes ensuring stability and high availability.
Interactions between the administrator and the cluster are done through Kubernetes API requests. They are administered by the master node, then validated and processed by the Kubernetes API server. The API server also runs all the internal processes of the cluster, tracks the status of all components and manages the exchanges between them.
The scheduler monitors the Kubernetes API server for newly created tasks and pods and organizes user pods to worker nodes taking into account resource requirements, data location, hardware and software policies, affinity specifications, deadlines, etc.
A key-value shop is a part of the control node, which is responsible for storing all the data of the Kubernetes cluster.
The Controller Manager monitors the current state of the controllers via the Kubernetes API server, compares it to the desired state and ensures that they match. It also runs the Node, Job, Endpoints, Service Account and Token controller processes.
The Cloud Controller Manager is required for integration with cloud technologies in case the Kubernetes cluster is running in the cloud. It runs controllers that are specific to the cloud service provider, including: node, route and service controllers.
Working nodes
The agents and core elements of the worker node provide the execution environment for the Kubernetes cluster.
Kubelet is run on each node in the cluster. It acts as a pipeline between the API server and the node, retrieving tasks from the server and ensuring that the containers are running in the user pod and functioning correctly.
Kube-proxy is a very important network component (running on each node as well as on Kubelet) that manages IP translation and routing. It monitors and controls compliance with network rules, enabling interaction between the internal or external network cluster and the User Pods.
The container runtime that runs or stops the containers is located in each worker node. This can be Docker, CRI-O, containerd or any other Kubernetes container runtime interface.
Additional components
- Infrastructure to work on: physical or virtual machines, private, public or hybrid clouds, etc.
- Container Registry for storing the container images on which the Kubernetes cluster is based
- Storage of application data attached to the cluster
Deploying a Kubernetes cluster on the Cloud
Given the rather complex architecture of the Kubernetes cluster, it can seem very difficult to deploy, manage and maintain it, requiring a separate service. With Hidora Cloud Platform, the Kubernetes Cluster solution is available for automatic installation with a few clicks.
1. Log in to your Hidora Cloud dashboard.
2. Navigate to the Marketplace (under the Clusters category).
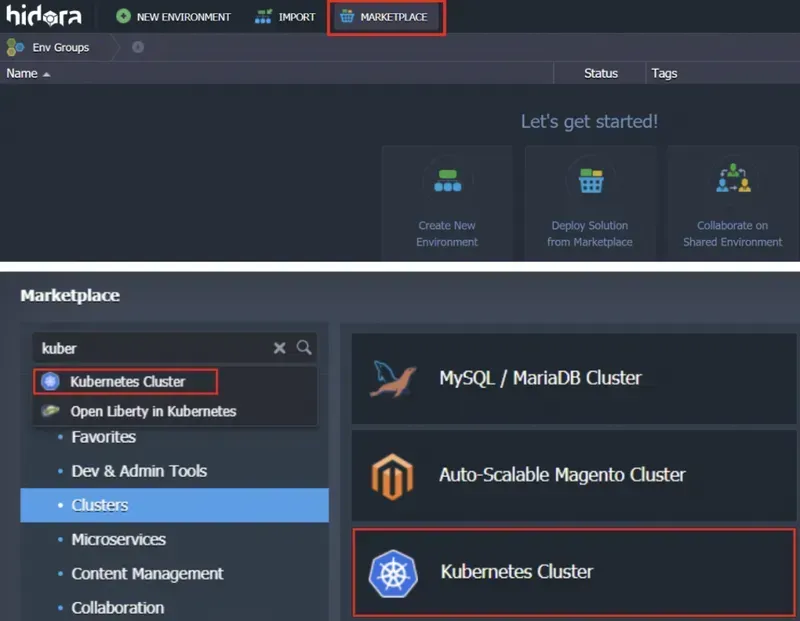
3. Find the Kubernetes cluster and specify your settings in the installation dialog box:
- Select a version of Kubernetes for your cluster.
- Choose the K8s dashboard
- Specify the required topology: development or production. The development topology consists of a control plane and a scalable worker node, the production topology consists of a multiple control plane with API balancers and scalable workers.
- Select the preferred input controller for your cluster (NGINX, Traefik or HAProxy).
- Choose a clean or custom cluster for your deployment
- Enable or disable dedicated NFS storage with dynamic volume provisioning (GlusterFS with three additional nodes)
- Add the modules you need, they can be activated later via the add-ons.
- Specify the name of your environment
- Provide an environment alias
- Select a region
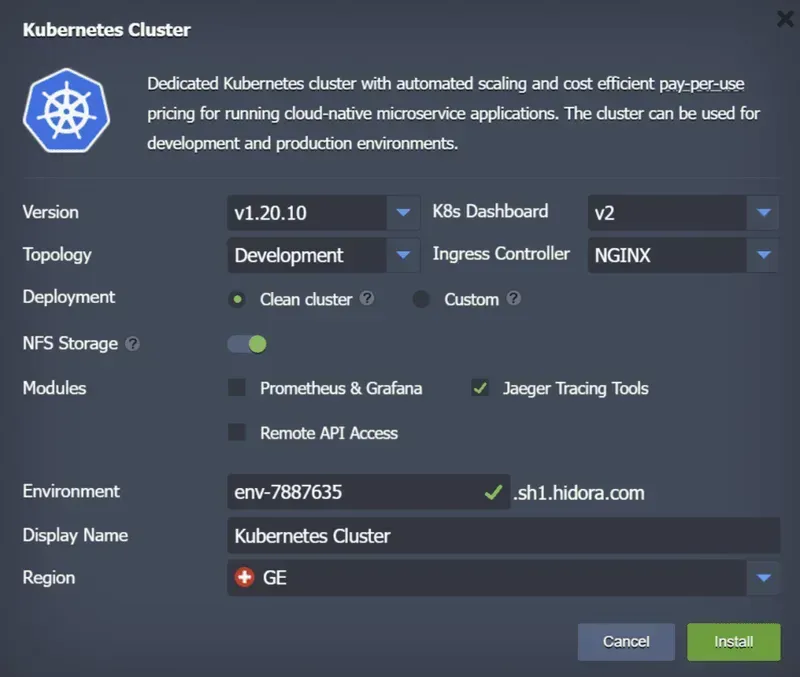
4. Click Install and within minutes, the Hidora Cloud Platform will automatically configure your Kubernetes cluster.
Hidora Cloud’s automation technologies ensure smooth integration and make it easy to work in a cloud environment.